SCRUBBER SYSTEM
The exhaust gases of combustion may contain substances considered harmful to the environment, and the scrubber may remove or neutralize those. A scrubber is used for cleaning air, fuel gas or other gases of various pollutants and dust particles. Scrubbing works via the contact of target compounds or particulate matter with the scrubbing solution. Solutions may simply be water (for dust) or solutions of reagents that specifically target certain compounds.
Process exhaust gas can also contain water-soluble toxic and/or corrosive gases like hydrochloric acid (HCl) or ammonia (NH3). These can be removed very well by a wet scrubber.
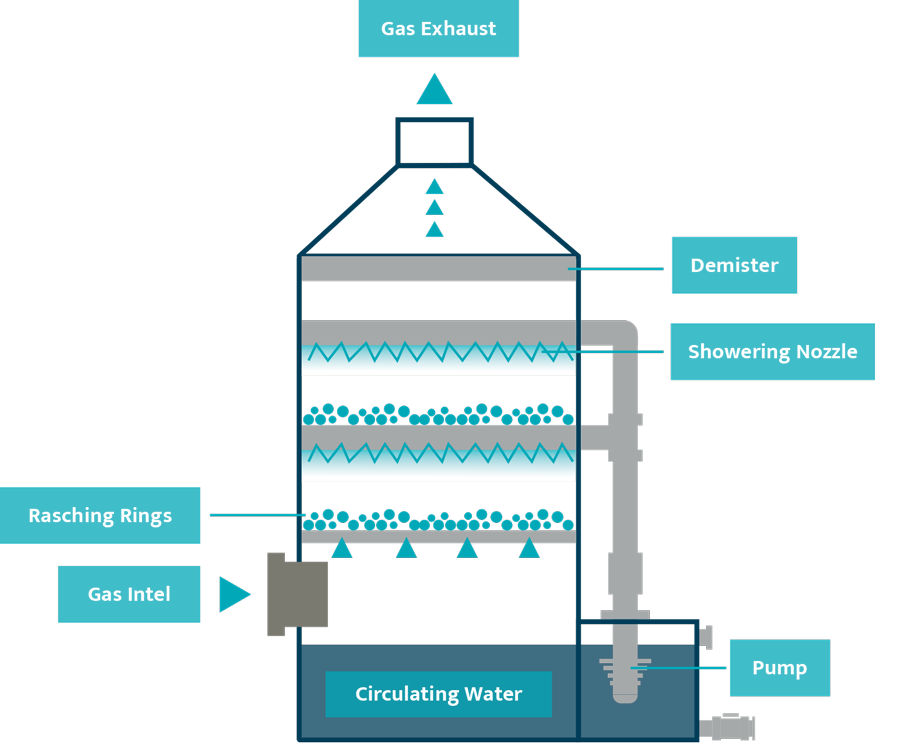
Removal efficiency of pollutants is improved by increasing residence time in the scrubber or by the increase of surface area of the scrubber solution by the use of a spray nozzle, packed towers or an aspirator. Wet scrubbers may increase the proportion of water in the gas, resulting in a visible stack plume, if the gas is sent to a stack.
Scrubber systems offer several advantages in air pollution control. They can effectively remove a wide range of pollutants, including acidic gases, particulate matter, and toxic substances. Scrubbers can also be designed to handle high-temperature and high-pressure gas streams. Additionally, some scrubbers have the capability to recover and recycle certain pollutants or by-products.
However, scrubber systems also have certain limitations. They require a continuous supply of liquid or chemicals for operation, and the disposal or treatment of the captured pollutants or waste water can be a concern. Scrubber systems can also have high capital and operational costs, depending on the specific design and requirements.
Overall, scrubber systems are important tools in reducing air pollution and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. The selection of a scrubber system depends on the specific pollutants to be controlled, the characteristics of the gas stream, and the desired level of pollution control.
KEY BENIFITS
- Effective Pollutant Removal
- Versatility
- High Removal Efficiency
- Flexibility in Pollutant Capture
- Compatibility with Hazardous Pollutants
- Compliance with Environmental Regulations